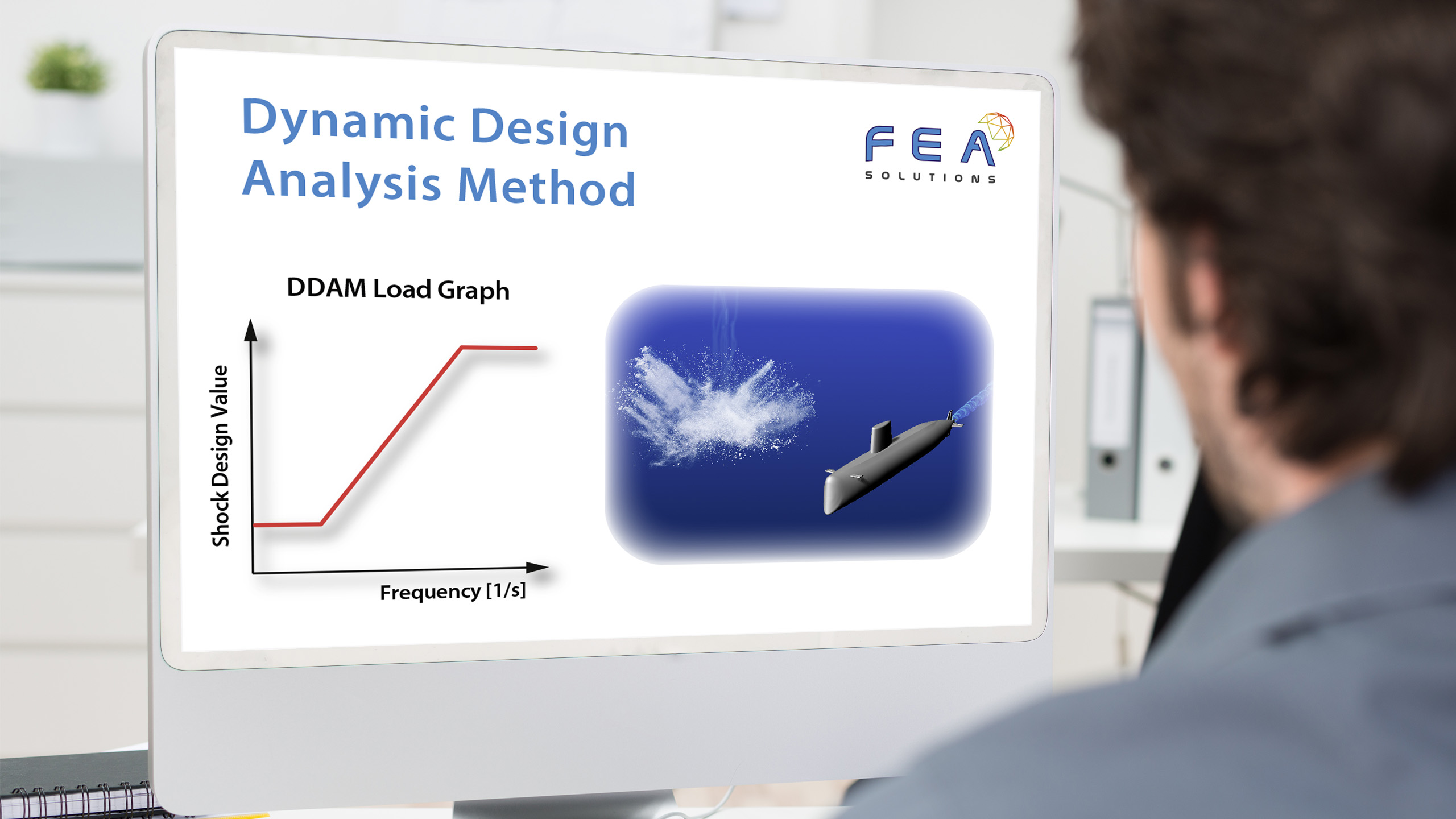
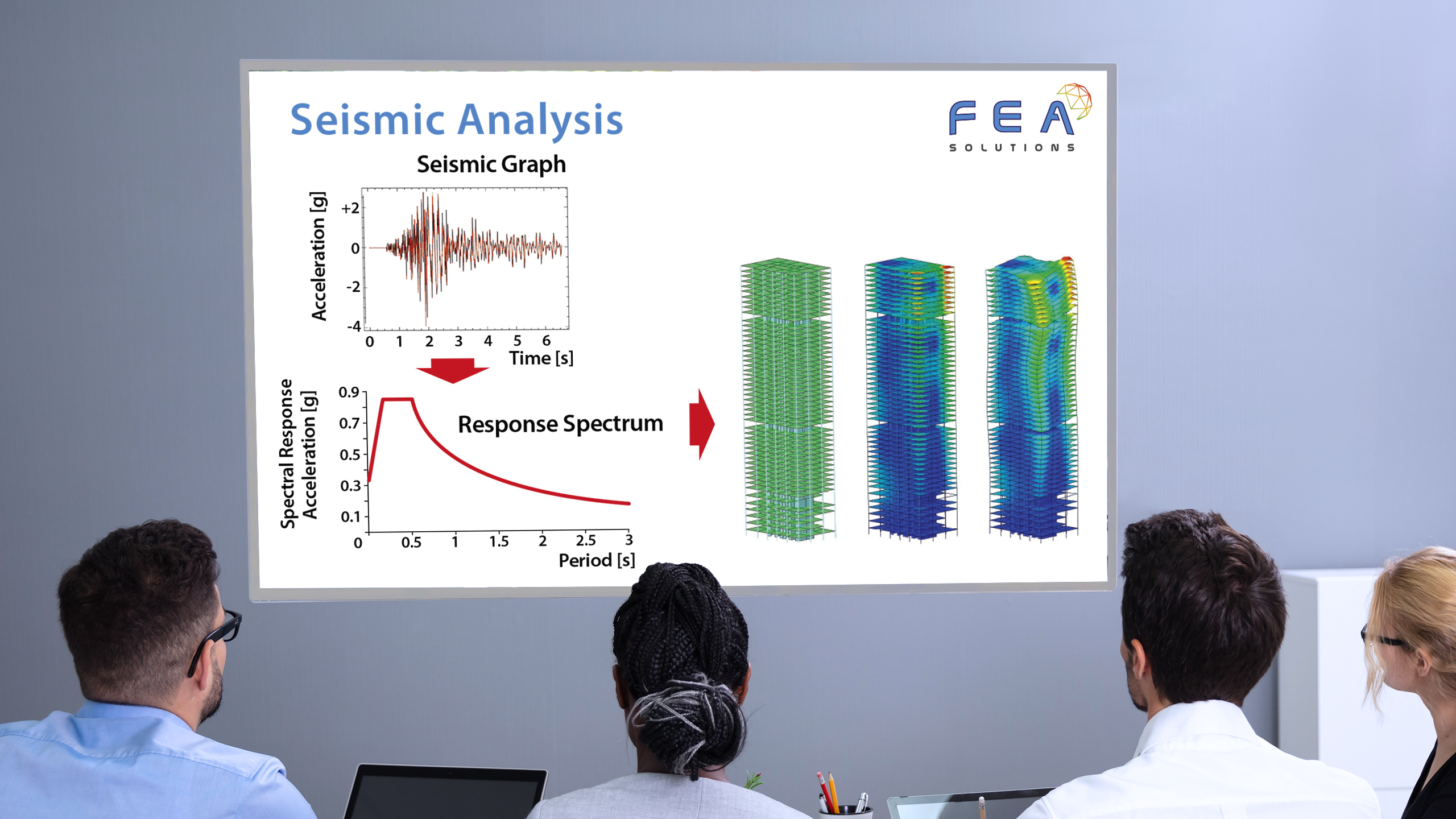
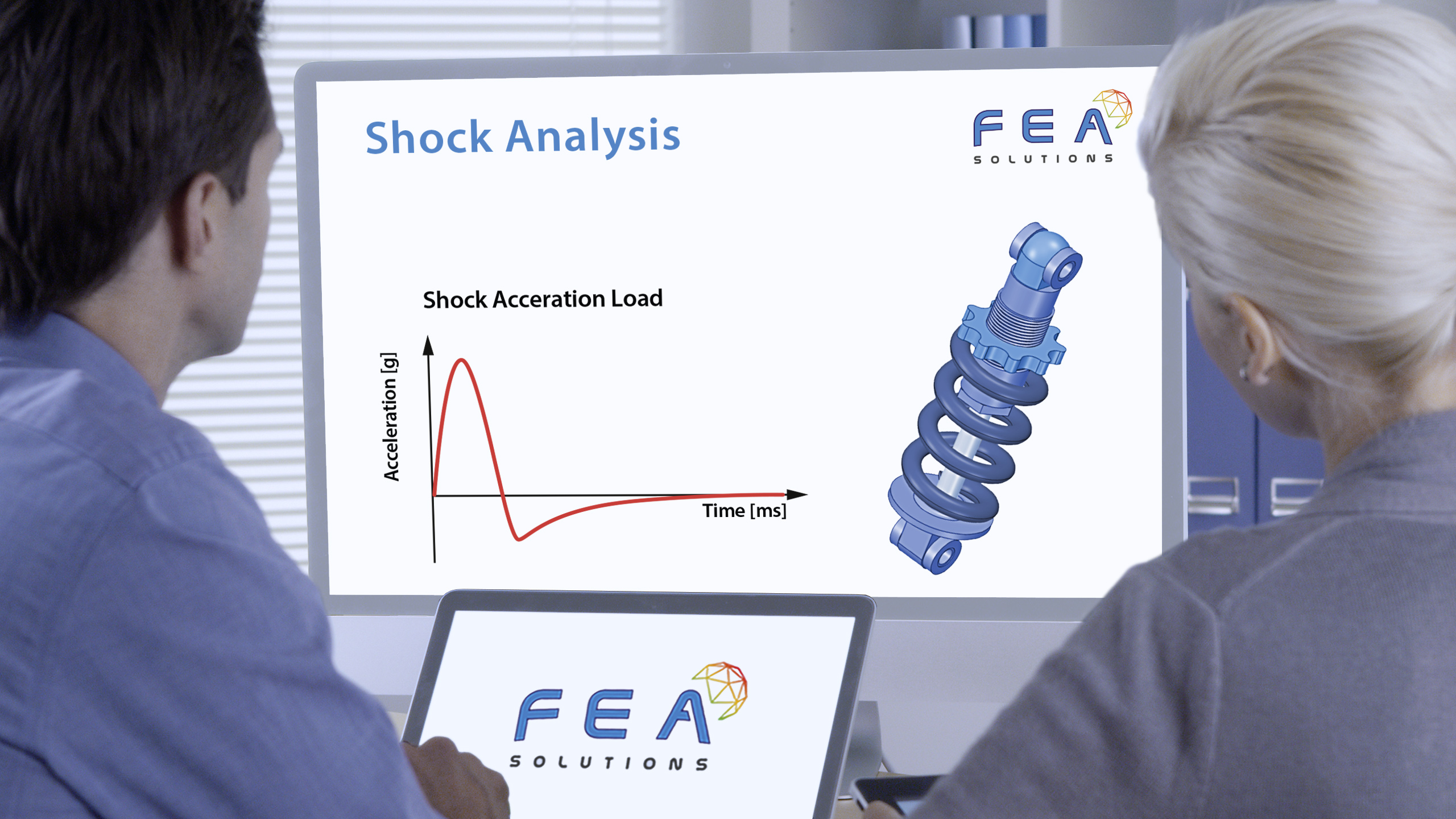
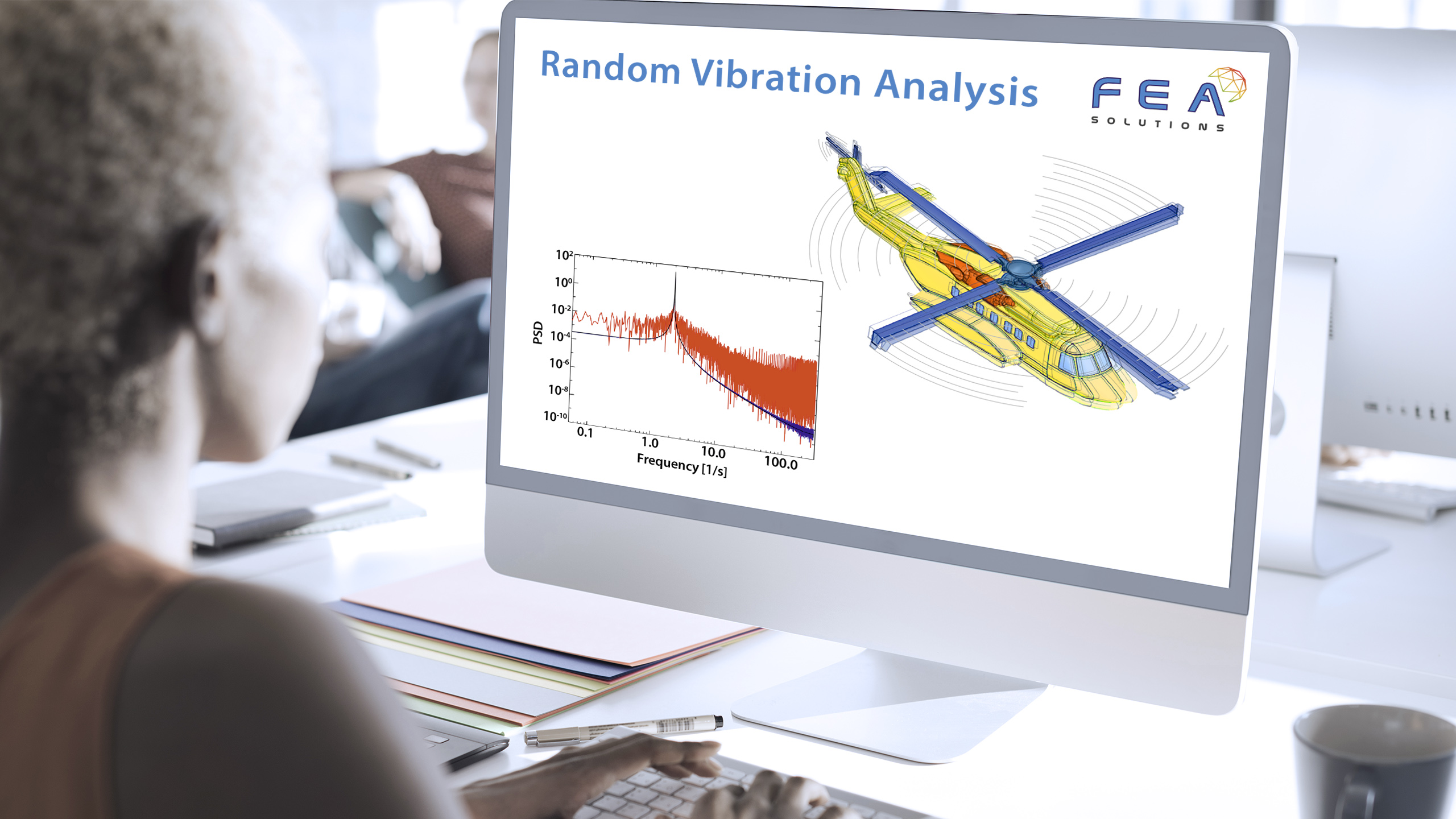
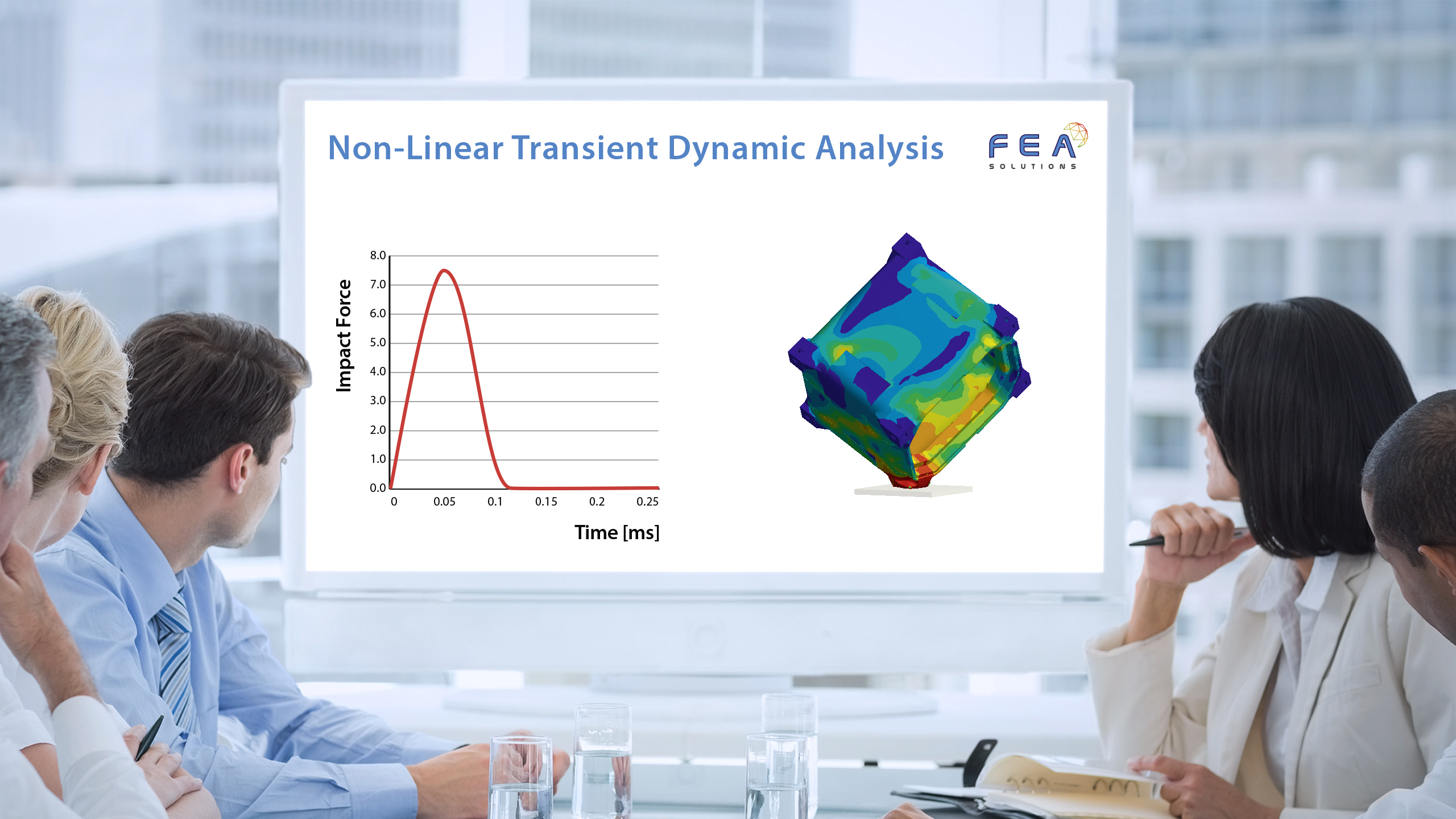
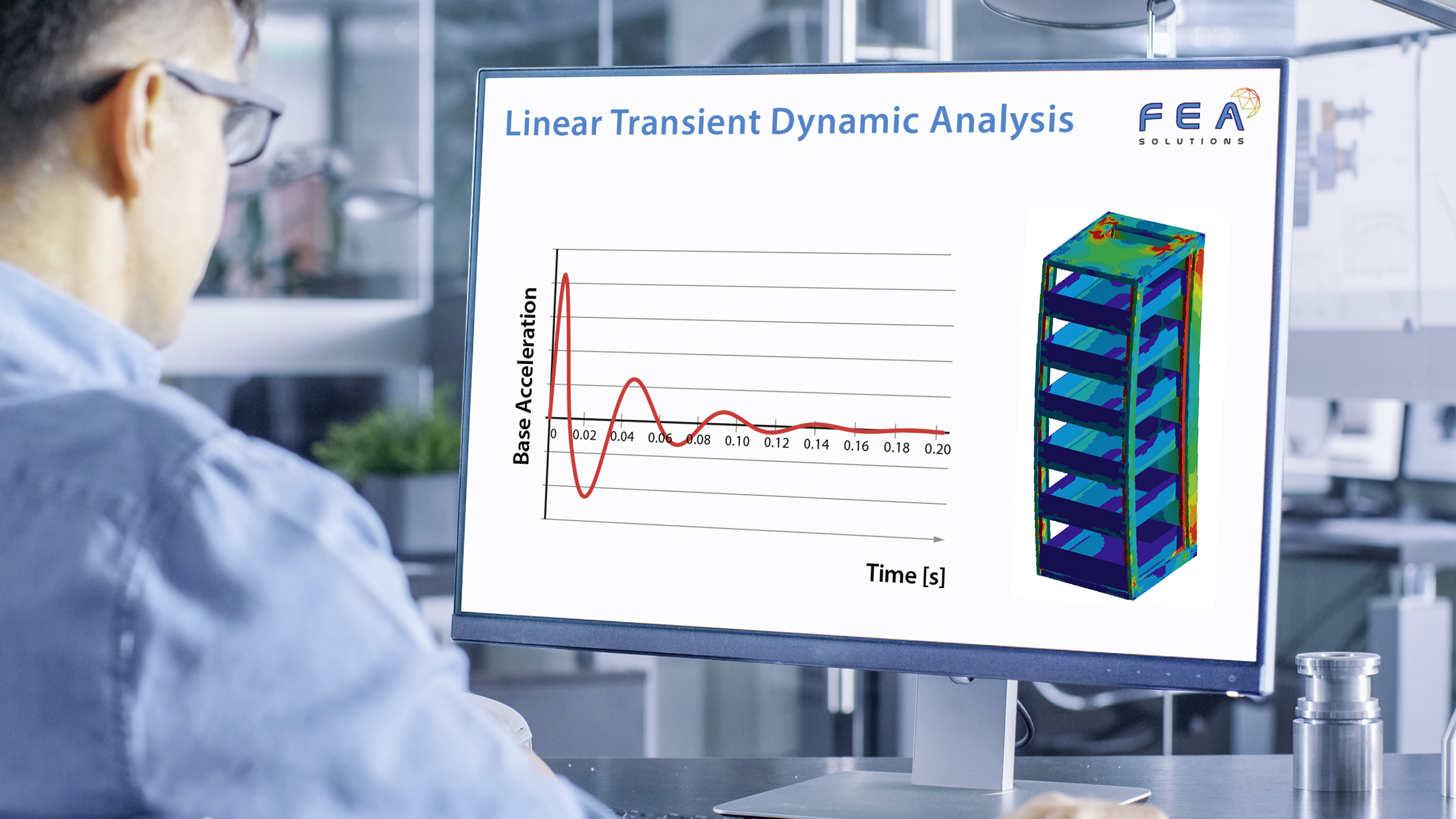
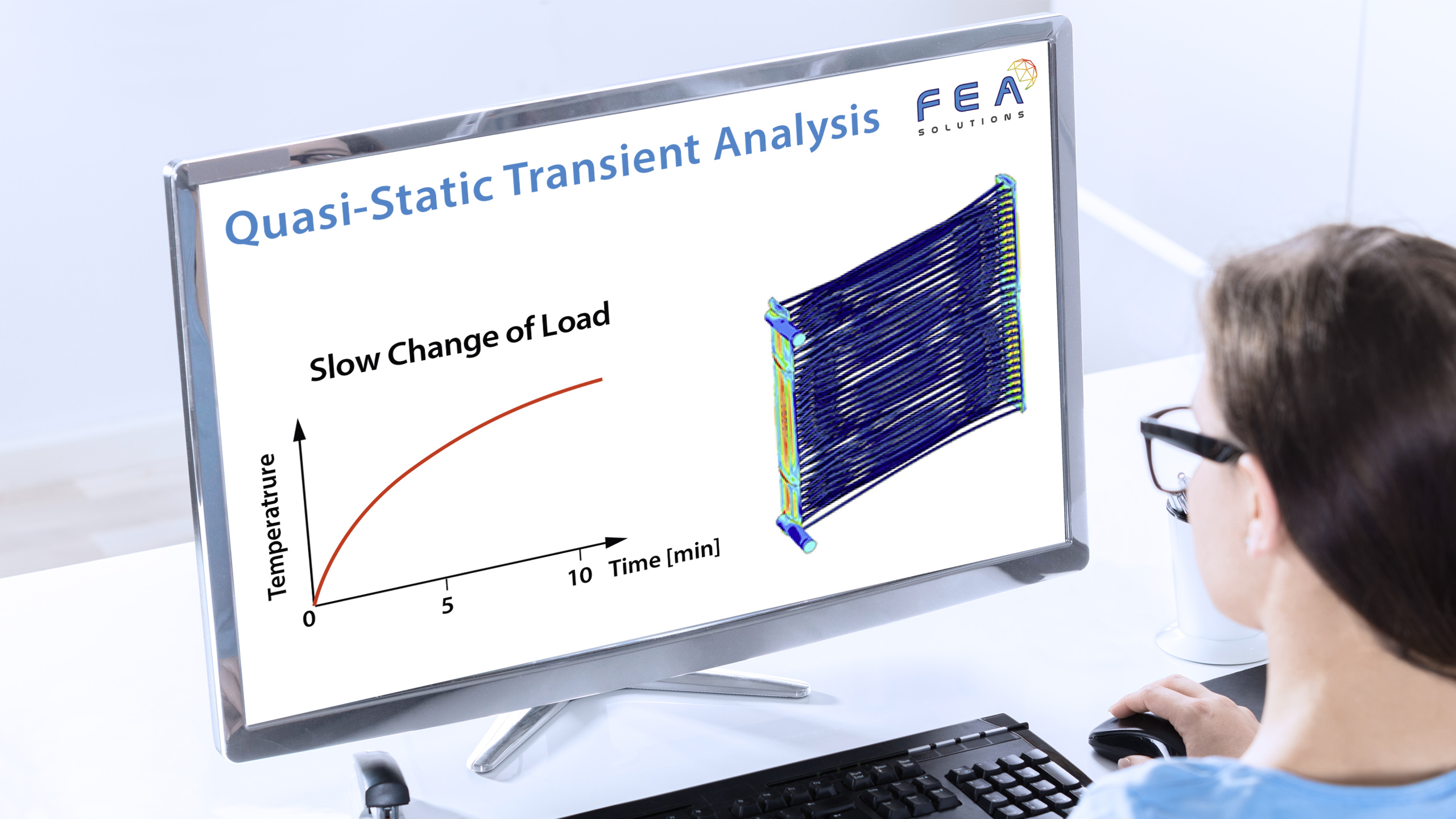
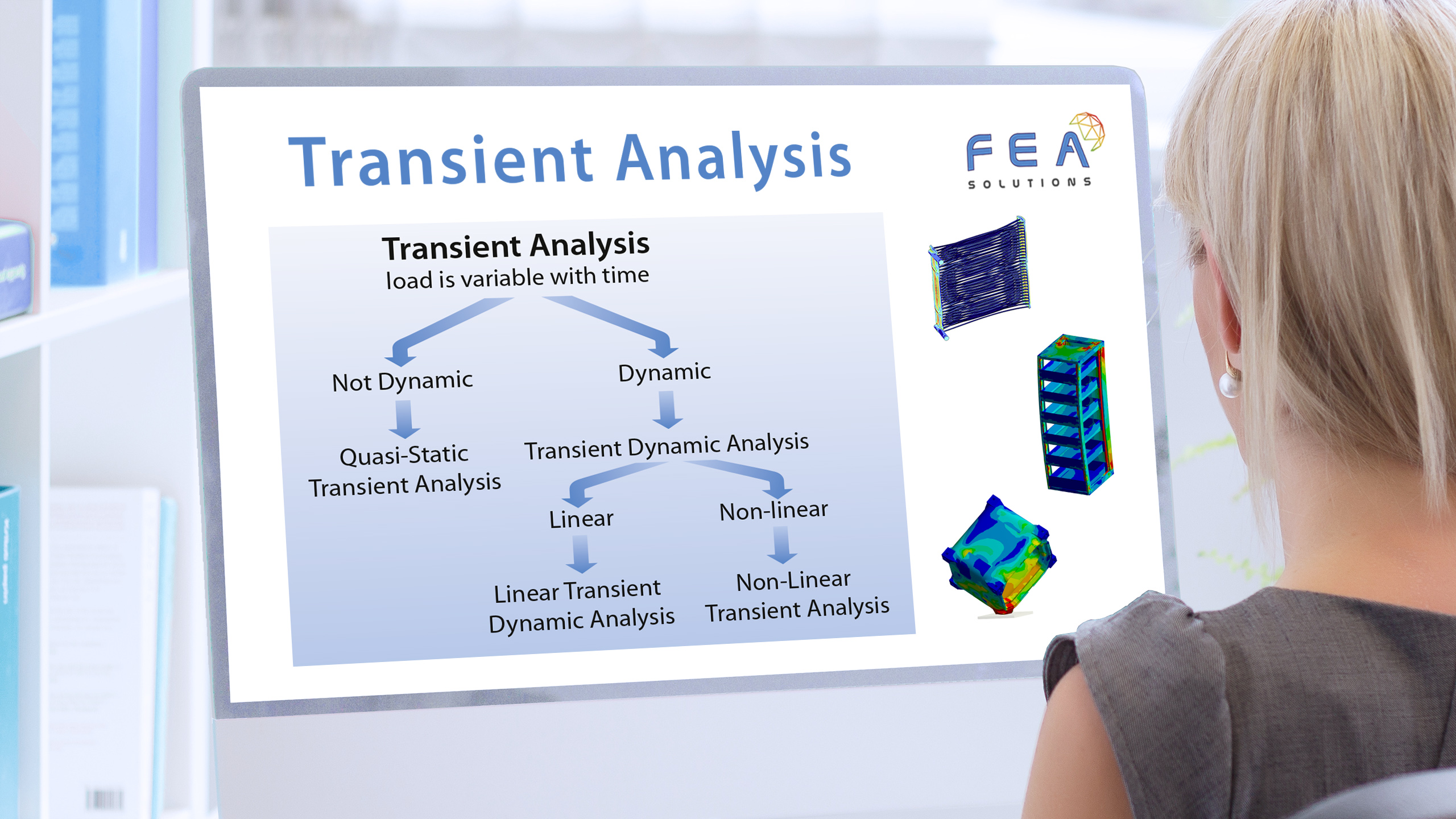
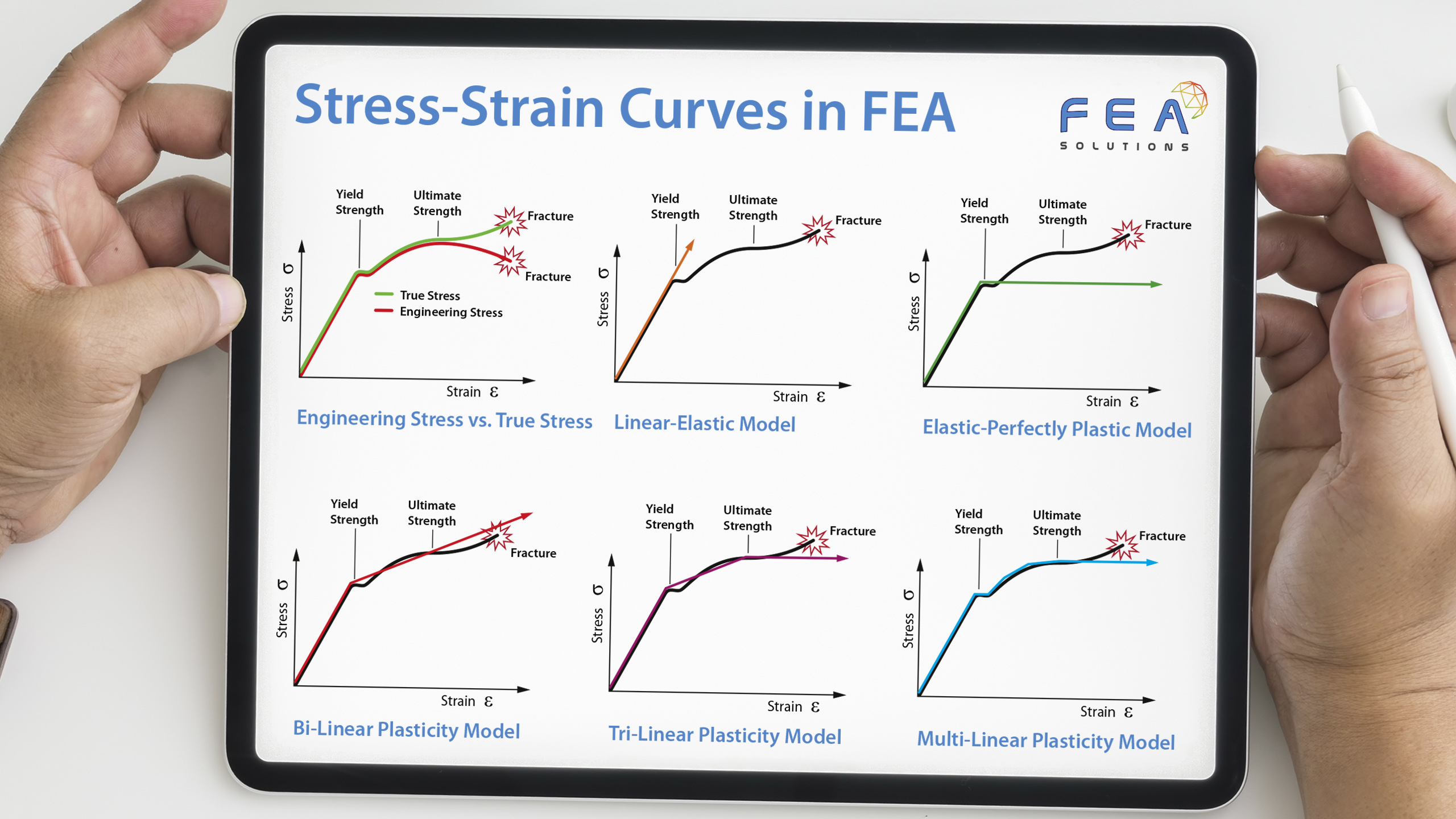
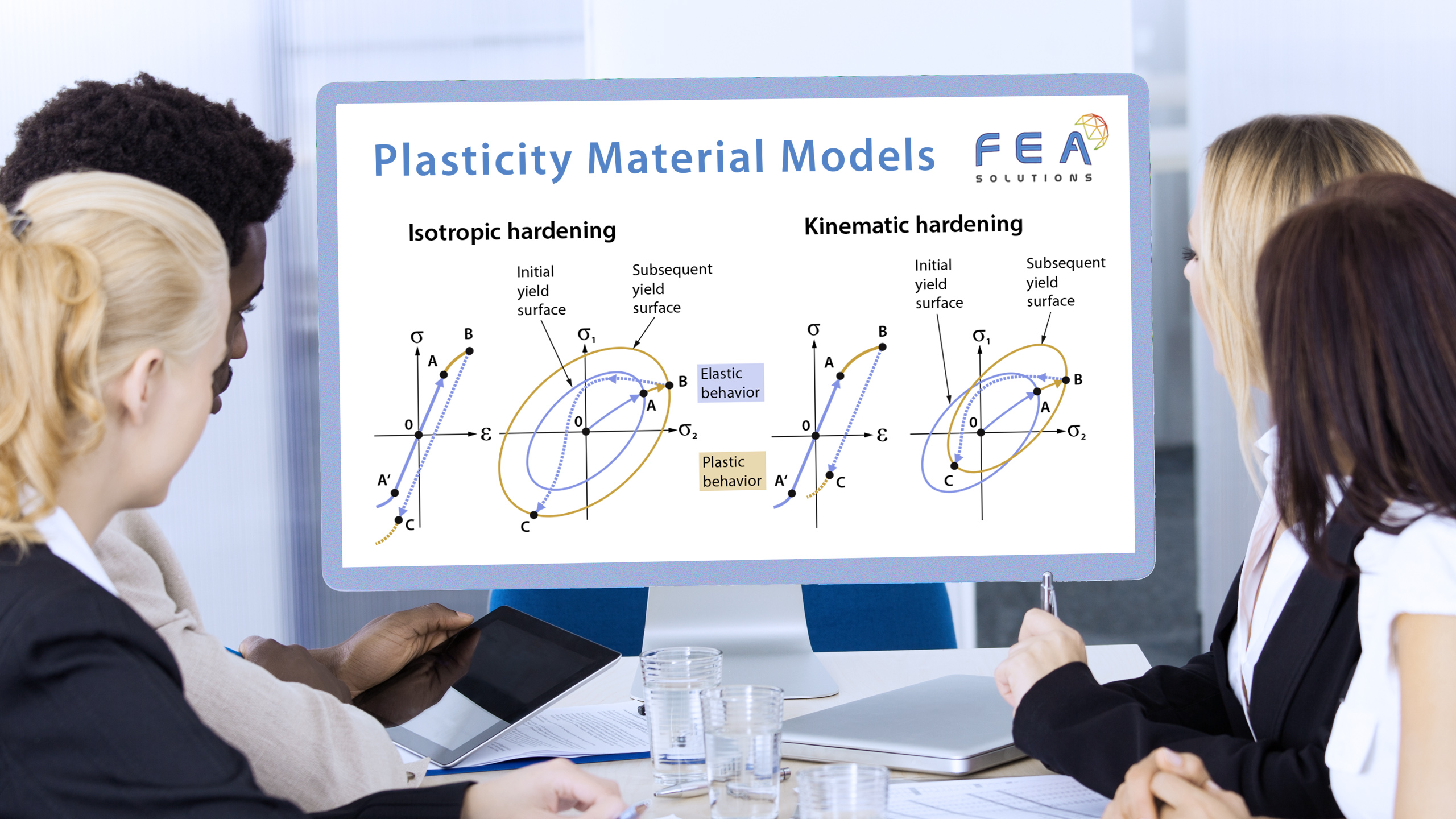
20 Nov Dynamic Design Analysis Method (DDAM)
The purpose of a Dynamic Design Analysis Method (DDAM) in FEA is to find a system's response to a shock load without the need for a shock curve (acceleration vs. time graph), using empirical correlations instead. The DDAM is used for the analysis of equipment...