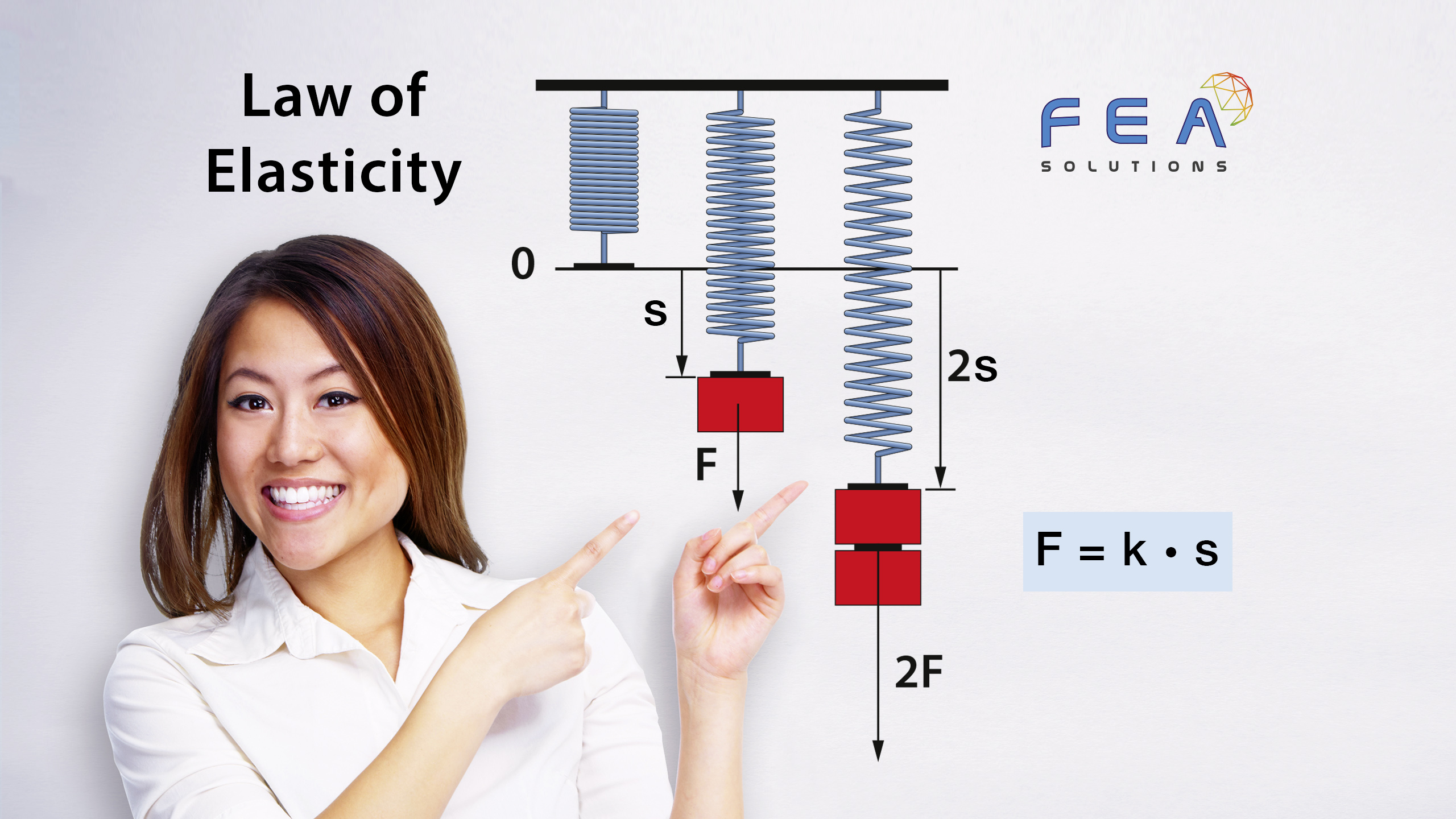
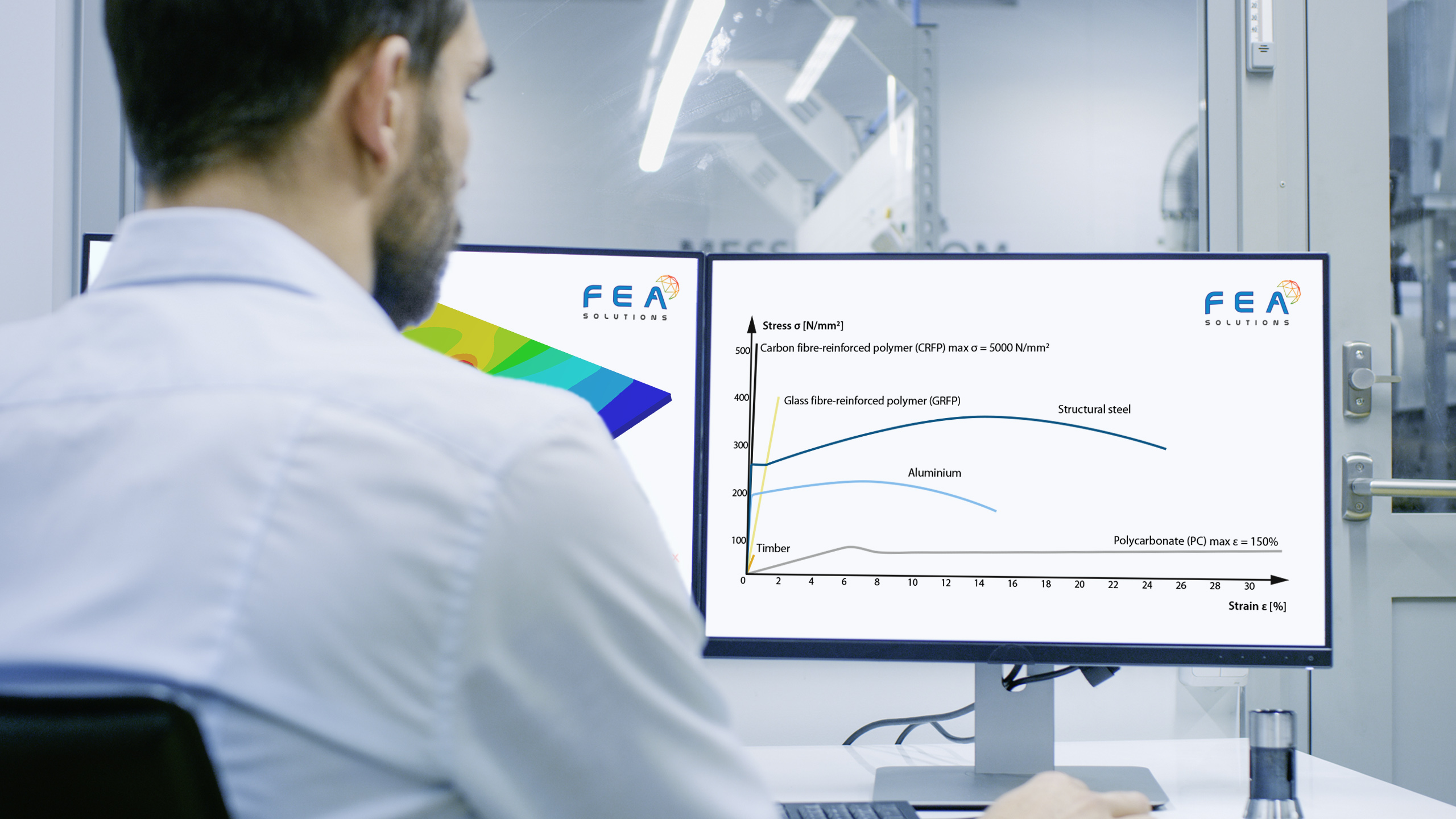
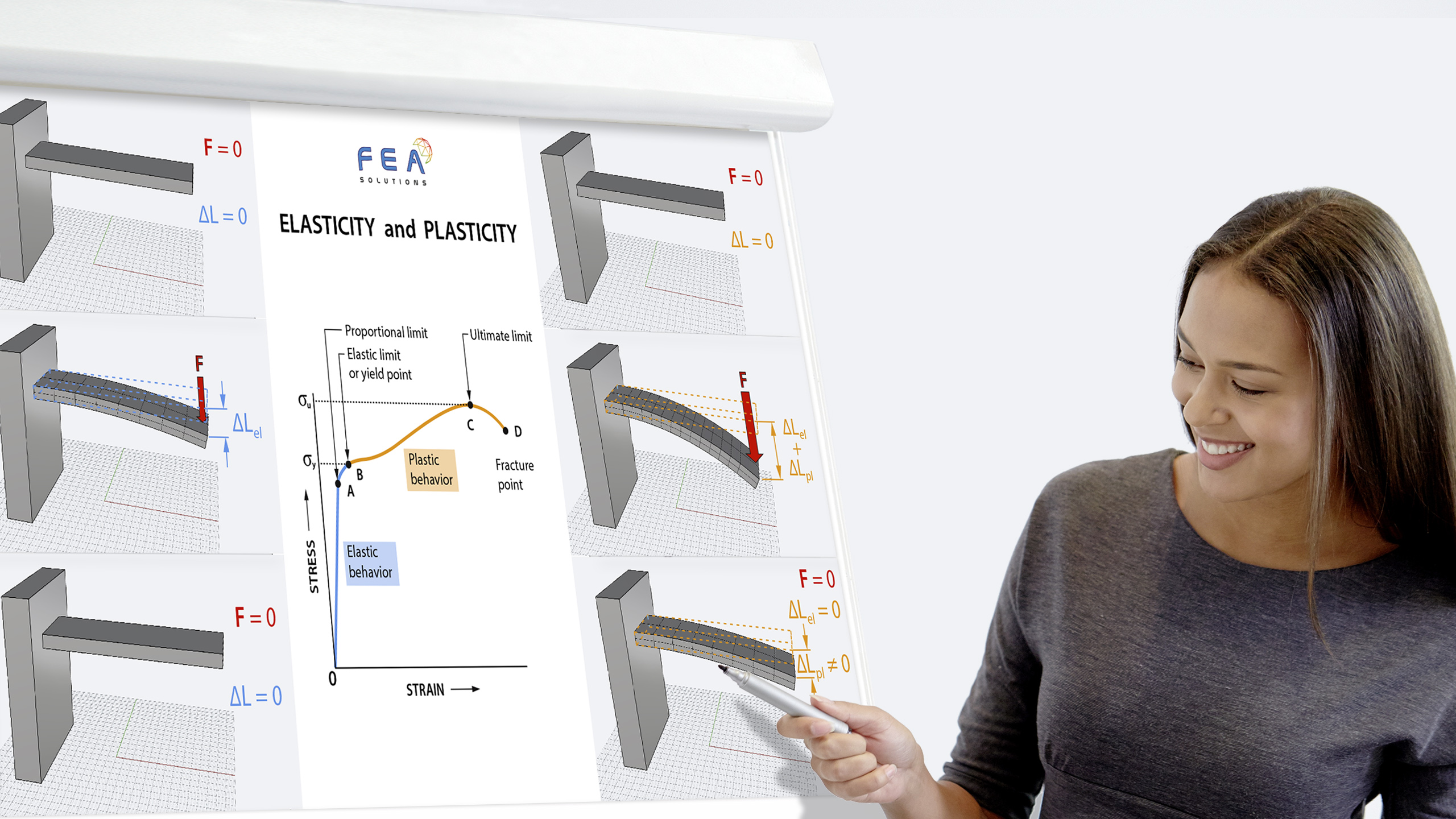
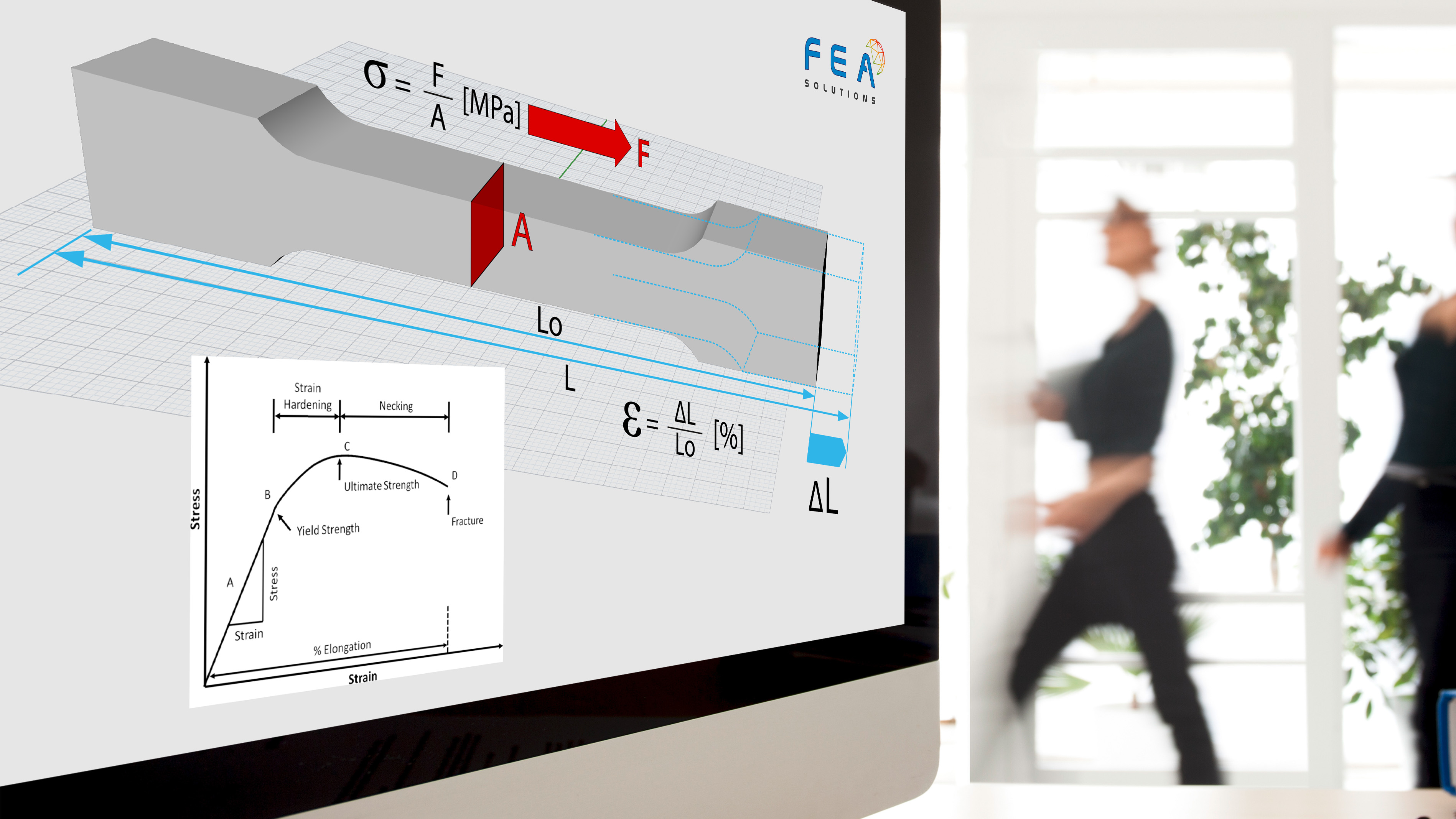
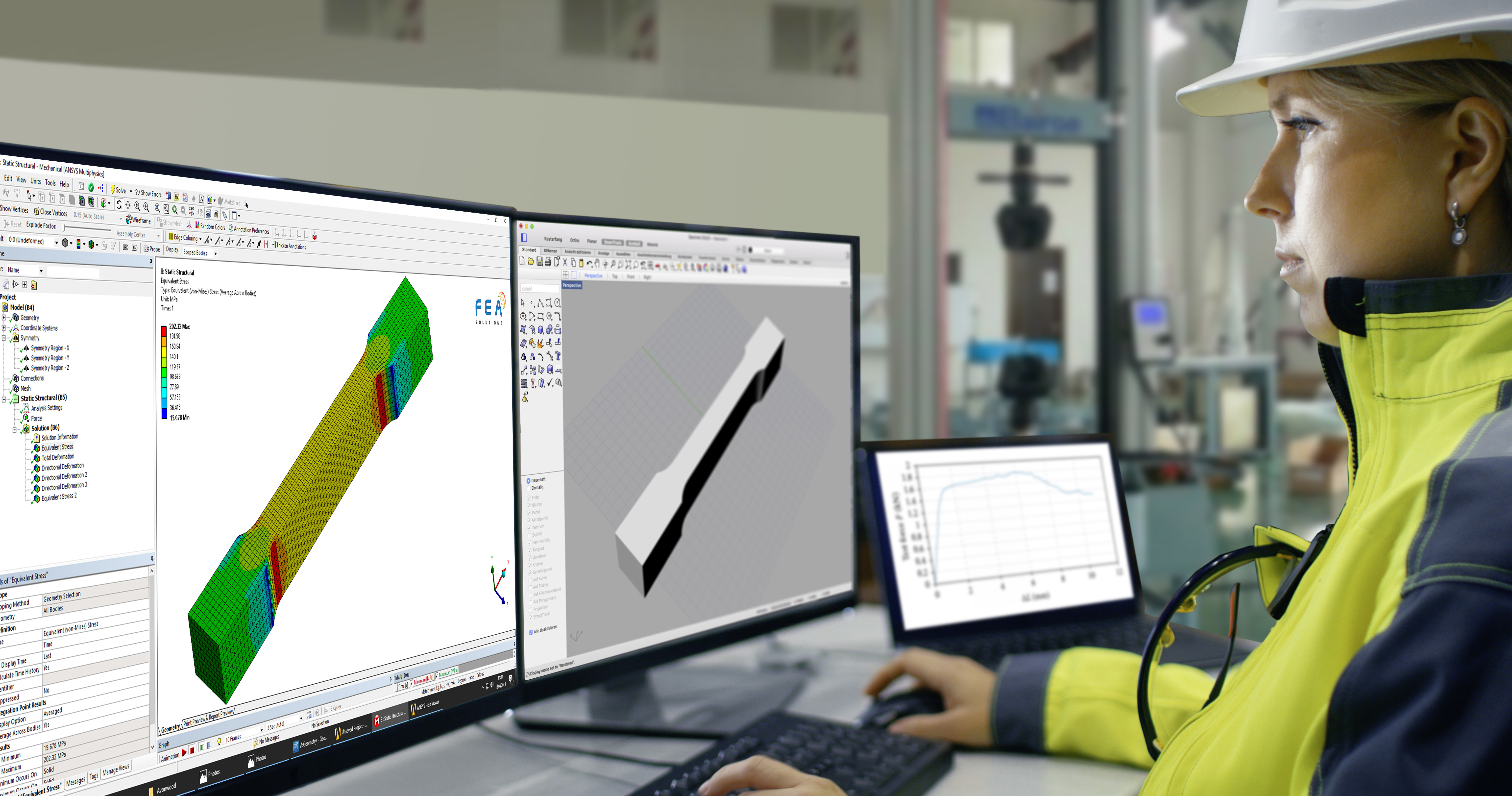
27 Jun Factor of Safety
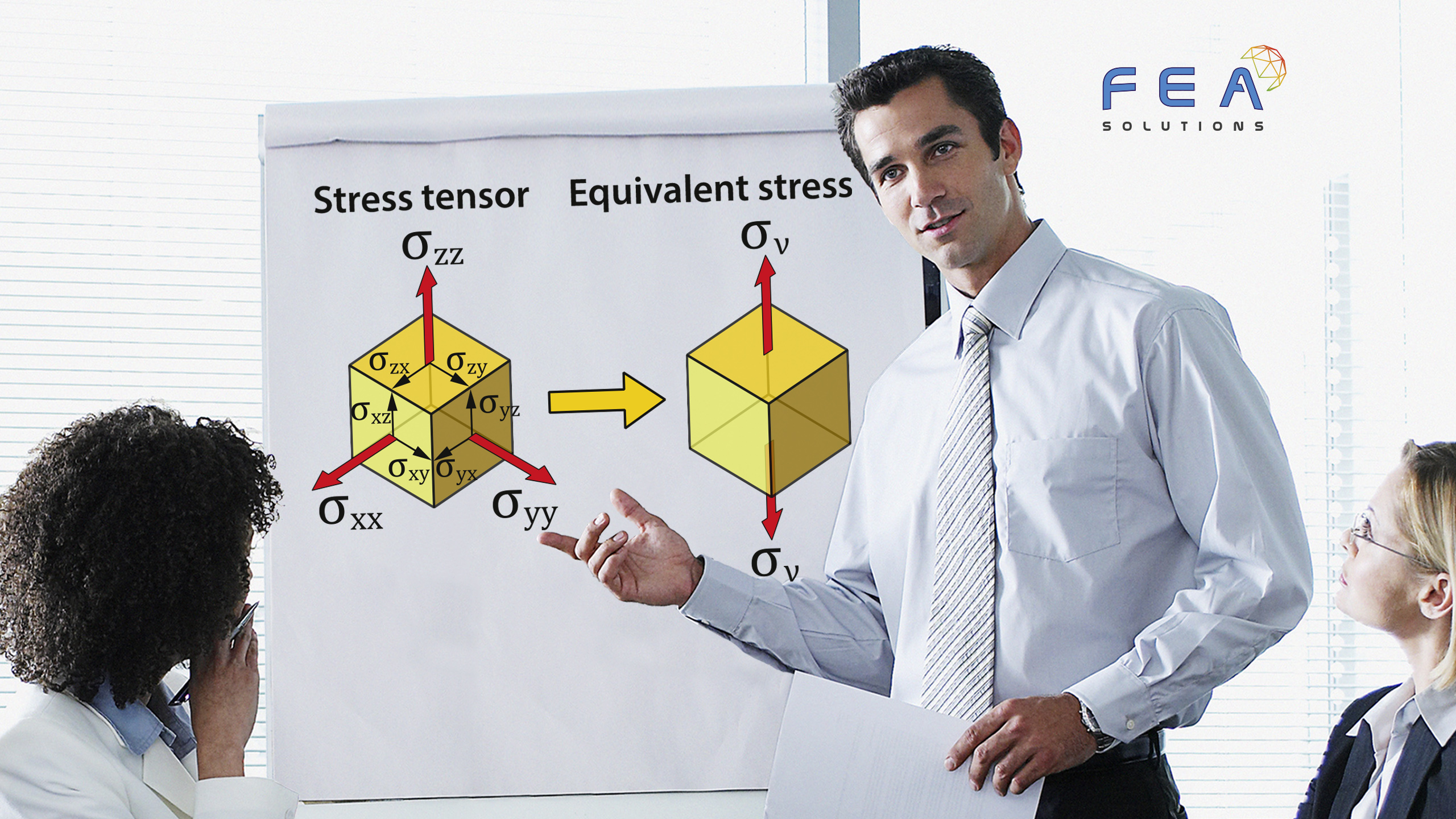
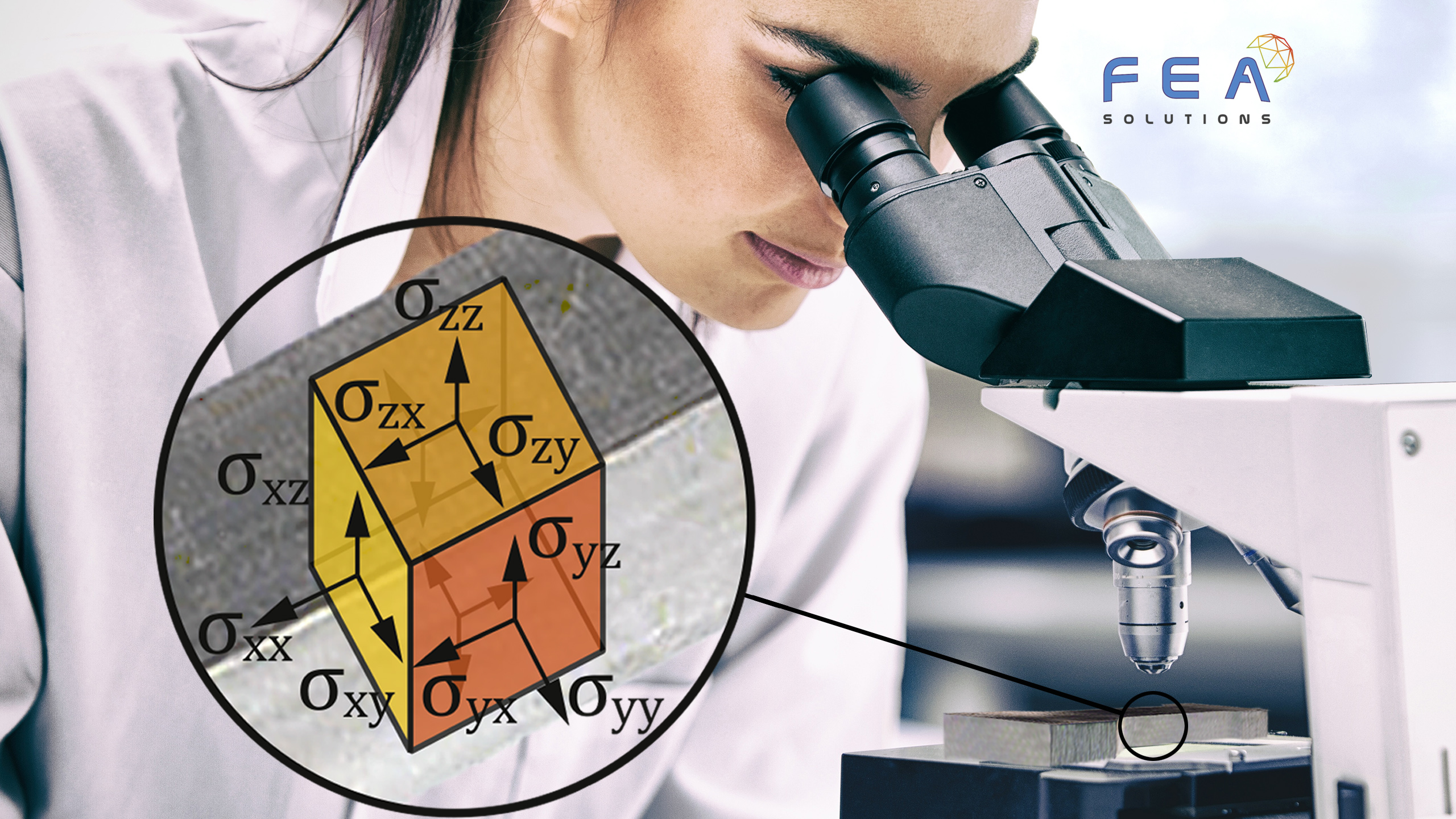
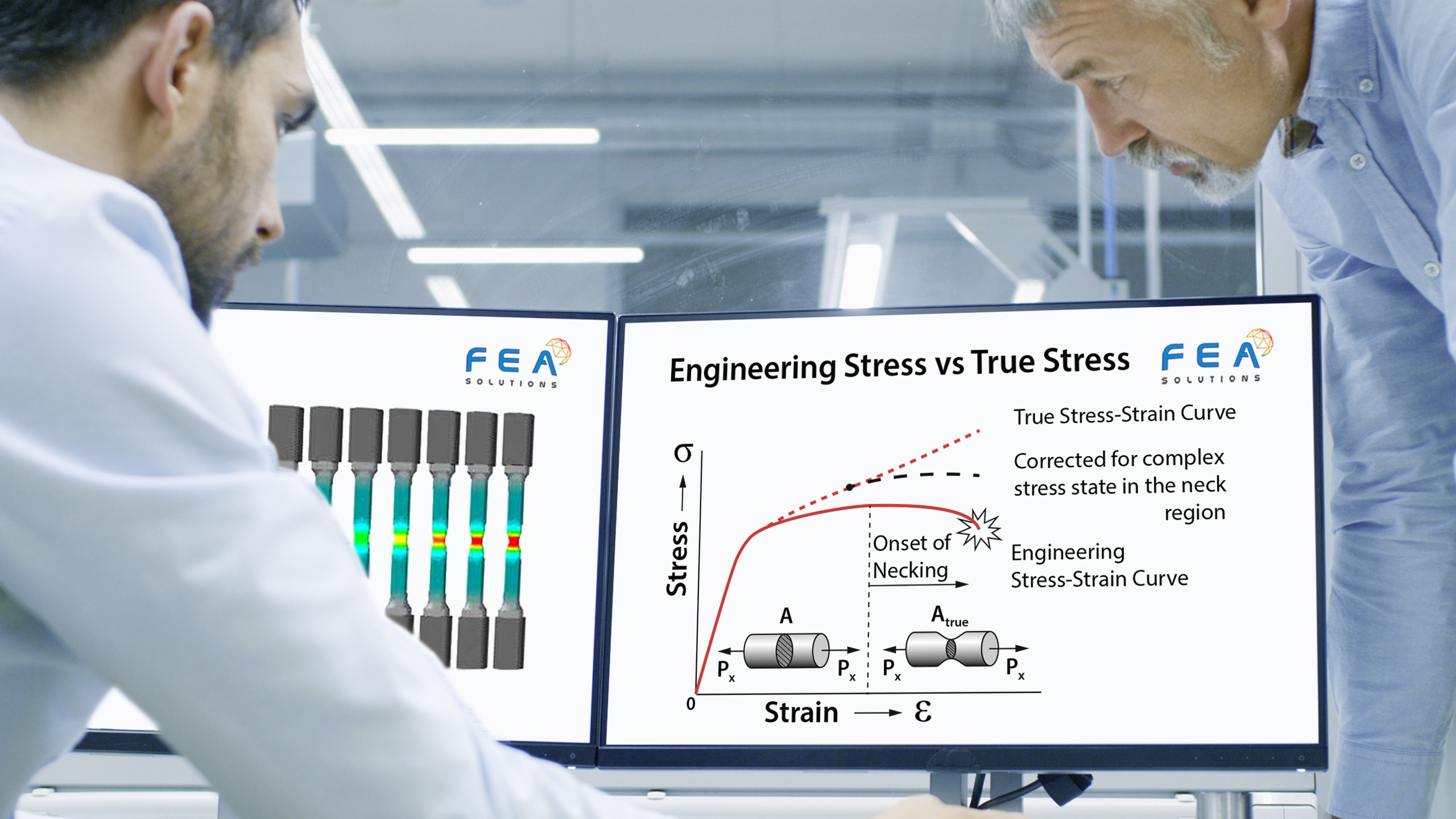
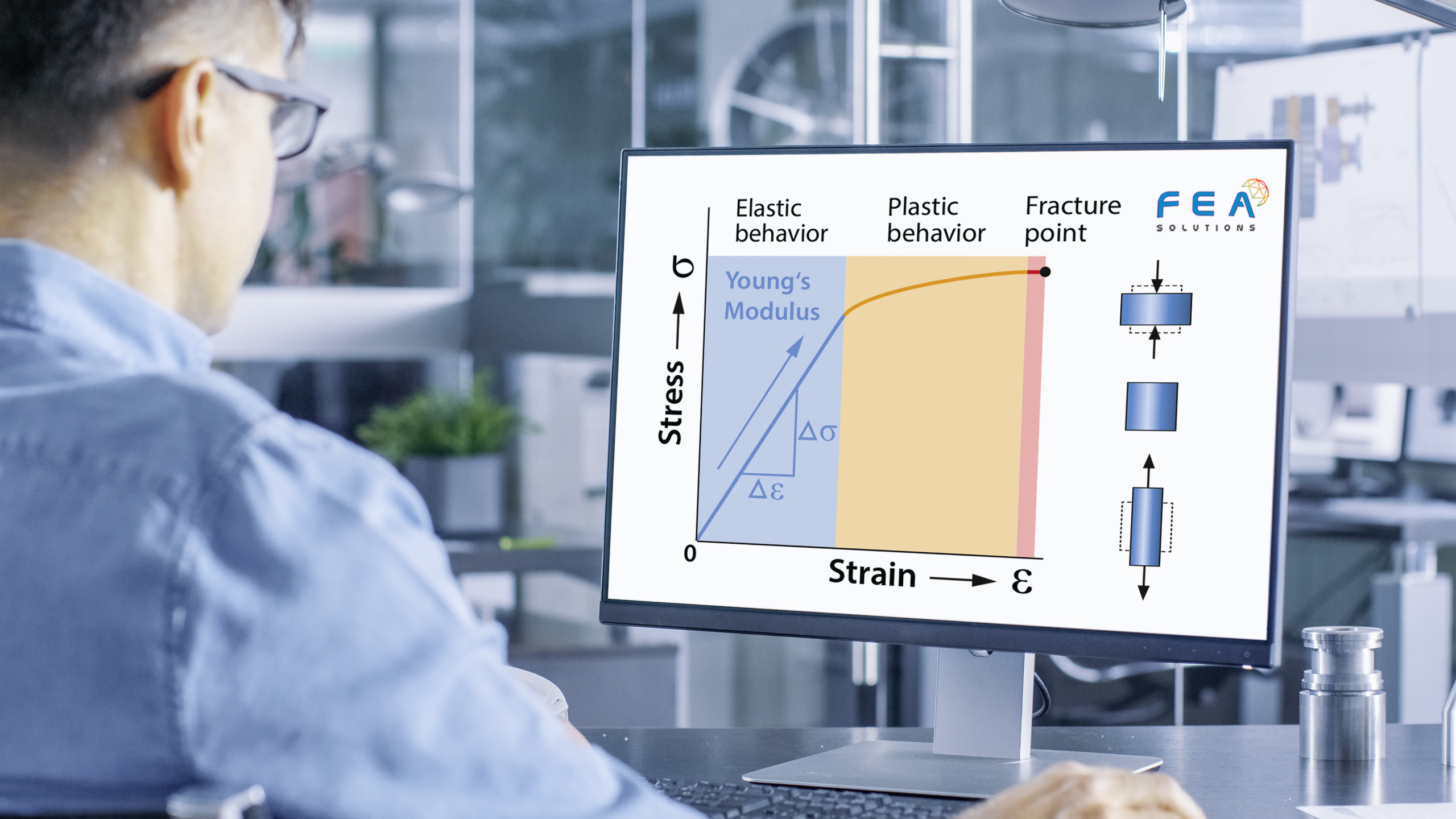
To assess if a structure is suitable for the intended purpose, the results of a FE analysis have to be compared to acceptance criteria, also called allowables. For a stress analysis, allowables could be e.g. equivalent stresses (see https://fea-solutions.co.uk/equivalent-stress/) or deflections. The Factor of Safety (FoS) is...