10 Jan 2D Models
A 2D model is taking advantage of symmetry that allows a 2D representation of the 3D structure.
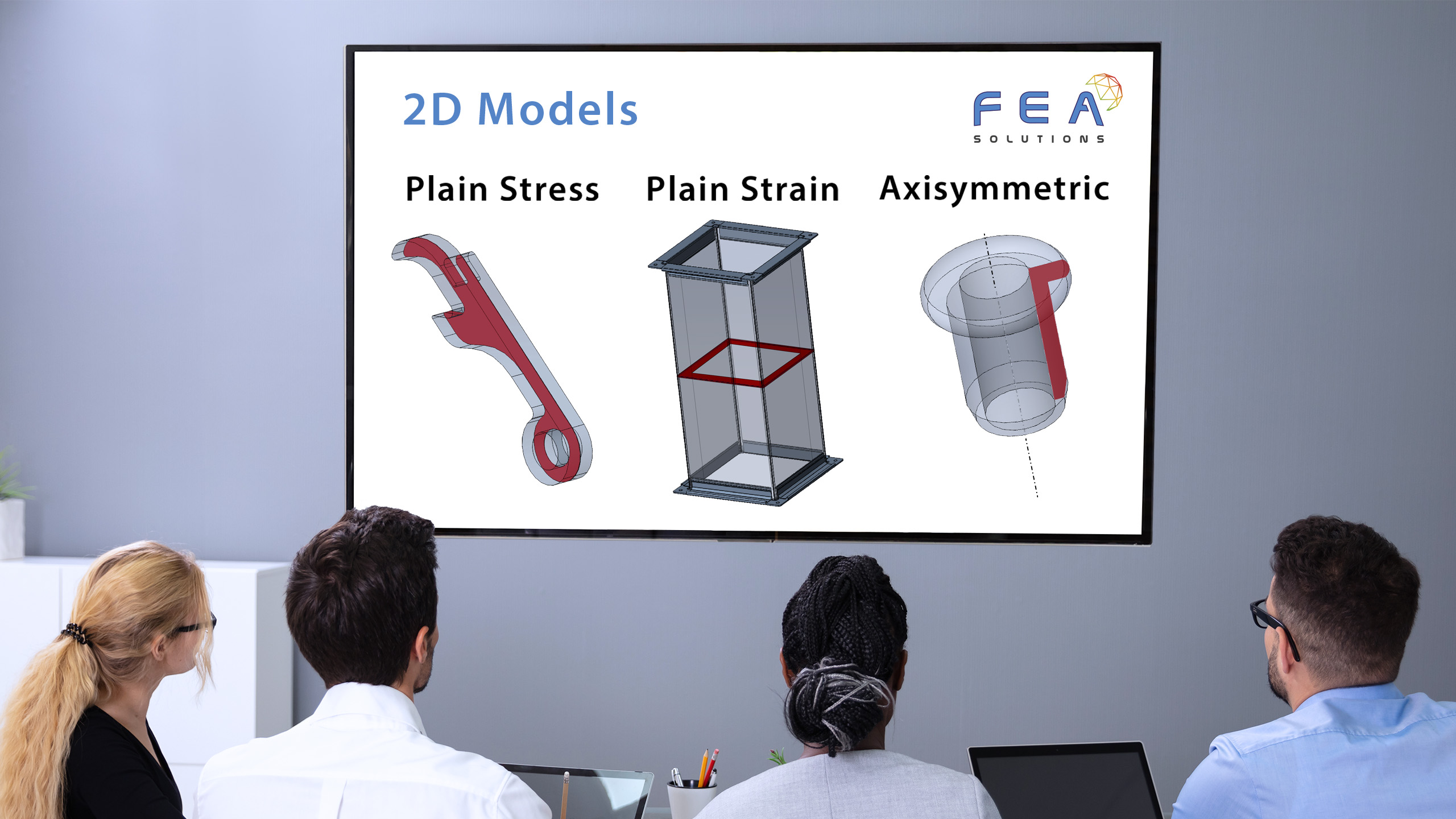
There are three types of 2D models that are used:
- Plane Stress. This represents a cross section of the model which is extending perpendicular to the 2D plane used. It assumes that the normal and shear stresses perpendicular to the body surface are zero.
- Plane Strain. This also represents a cross section of the model which is extending perpendicular to the 2D plane used. This model assumes that the out of plane geometry is large and/or constrained. It also assumes that loading does not vary in the out of plane direction.
- Axisymmetric. This model represents a cross section of a structure which extends rotationally along an axis, such as a cylinder. This 2D model assumes that the loads are also axisymmetric, meaning the loads are axial, radial, a uniform pressure or a uniform thermal expansion.
Please call us today on +44 (0)1202 798991 for any engineering analysis requirements you might have.
